The Role of Immutability and Air-Gapping in European Data Protection Strategies
Table of contents
European data protection is undergoing a quiet but radical shift. Once centered on legal compliance and checkbox auditing, it is now a high-stakes game of cybersecurity resilience. The rise of sophisticated ransomware, targeted attacks on backup systems, and the rapid expansion of cloud and IoT infrastructure have left organizations vulnerable, even those that believe they are prepared.
Regulatory evolution, like the GDPR and the new Data Act, reflects this new reality: data must be protected, recoverable, reliable, and continuously available.

This post explores two critical technologies that have emerged as strategic defenses in this environment: immutability and air-gapping. For European businesses facing a growing cyber threat landscape, they are increasingly essential to both compliance and continuity.
The Expanding Web of European Data Regulations
The EU’s data protection framework continues to evolve in scope and complexity:
- GDPR emphasizes privacy and security. Article 32 mandates the ability to promptly restore availability and access to personal data in the event of a technical or physical incident.
- ISO/IEC 27001 now includes enhanced cloud and SaaS protection measures, targeting resiliency in modern infrastructure.
- The Data Act, applicable from September 2025, shifts the conversation toward accessibility, fairness, and transparency in data usage. It mandates secure and user-controlled access to data from connected devices, raising the bar for secure data handling.
These regulations are not mutually exclusive. Together, they push organizations toward architectures that can retain data securely, enable user access and deletion, and maintain business continuity even in a crisis.
Why Backups Alone No Longer Cut It
Backups have traditionally been a fallback option, essential but passive. Unfortunately, attackers have caught up. A 2024 report on cyberattacks and ransomware shows that over 2 million cases of breaches were recorded from 556 publicly disclosed breaches in the EU.
Modern ransomware now encrypts production data and actively seeks out and destroys backup files and infrastructure. For example, some ransomware strains include scripts designed to locate Veeam or Hyper-V backups and corrupt or delete them. Others exploit admin credentials to access and erase snapshots or backup volumes. Once this happens, even the most comprehensive backup strategy is rendered useless.
This is where immutability and air-gapping enter the equation.
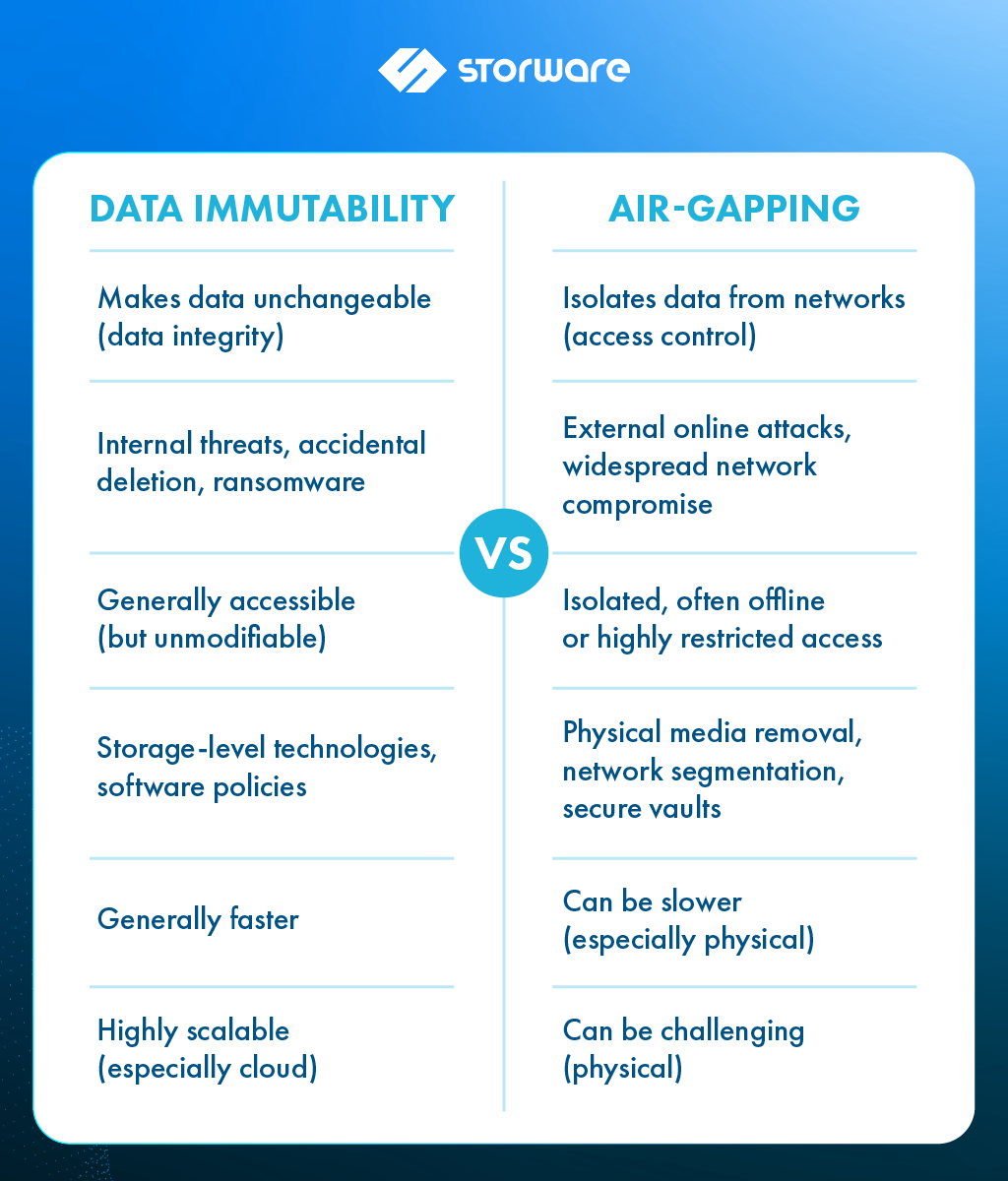
What Is Immutability?
Immutability is the ability to store data in a way that cannot be altered, deleted, or overwritten for a defined retention period. Data kept on immutable storage stays exactly as it is—tamper-proof and time-locked once written.
Key Benefits:
- Ransomware protection: Attackers cannot modify or delete immutable backup files.
- Compliance-ready: Meets retention requirements under GDPR, financial, and healthcare regulations.
- Audit integrity: Immutability ensures logs and data are preserved without risk of tampering.
How It Works:
- On-premises: WORM-enabled NAS or object storage.
- Cloud: Amazon S3 Object Lock, Microsoft Azure Immutable Blob Storage.
- Backup software: Veeam, Commvault, and others now support immutable backup repositories.
What Is Air-Gapping?
Air-gapping, particularly with relation to the internet, is the process of separating a system or network from unprotected networks. In data security, it refers to either physically (offline) or logically (network-segmented with rigorous access restrictions) storing backup copies in an environment totally separate from any production network.
Types of Air-Gapping:
- Physical: Offline tapes or disks, manually disconnected from the network.
- Logical: Isolated systems or networks with strict access controls, segmentation, or one-way data transfer mechanisms.
Key Benefits:
- Ultimate isolation: Prevents lateral movement of malware to backups.
- Survivability: Data remains safe even in the case of a full production environment compromise.
- Resilience during disasters: Ensures recovery capacity even when networks are down or compromised.
Comparison Table: Traditional Backups vs. Immutability vs. Air-Gapping
| Feature | Traditional Backups | Immutability | Air-Gapping |
| Ransomware Protection | Low | High | Very High |
| Compliance Support | Basic | Strong (supports audit trails) | Strong (ensures data isolation) |
| Recovery Reliability | Uncertain (can be tampered with) | High (unalterable copies) | High (offline or isolated backups) |
| Network Exposure | Always online | Online but locked | Offline or segmented |
| Deployment Complexity | Low | Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Cost | Low to Moderate | Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Use Case Fit | General, low-risk environments | Healthcare, finance, and legal sectors | Critical infrastructure, manufacturing |
Together, they provide layered protection. Immutable backups protect against tampering, while air-gapping ensures backups remain unreachable by attackers.
Use Cases in European Business Environments
SaaS Providers and Cloud Services
Companies hosting customer data under GDPR must ensure availability and recoverability. Combining immutable snapshots with logically air-gapped storage helps meet resilience and compliance requirements.
Manufacturing and IoT-Driven Sectors
With the Data Act mandating user access to IoT-generated data, manufacturers must store and protect vast volumes of telemetry. Immutability ensures these datasets remain accurate and auditable; air-gapping protects against targeted OT attacks.
Healthcare and Public Sector
These sectors are highly regulated and often targeted by ransomware. Immutability secures patient records against tampering, while air-gapping ensures continuity even during a breach.
Agriculture and Smart Infrastructure
Farmers using precision agriculture tools generate sensitive location and environmental data. Air-gapped storage can help protect this data from being exploited, while immutability ensures it remains accurate for subsidies, audits, or sustainability reports.

Preparing for the Future: Security Meets Regulation
The Data Act is pushing organizations to open up their data, but doing so without compromising security will be the real challenge. With the EU emphasizing accessibility and user rights, businesses must find ways to share data without increasing exposure.
Immutability and air-gapping provide the foundational safeguards to enable this. They ensure that data is unaltered even if it is widely shared. And even in cases of network breaches, a secure, offline recovery path exists.
In this way, these technologies are not just about cyber defense. They are enablers of digital trust, the cornerstone of Europe’s data-driven future.
Final Thoughts
European data protection strategies are evolving toward a model that assumes breach readiness as much as it assumes legal compliance. Immutability and air-gapping are central to this paradigm. When implemented correctly, they help businesses meet their obligations under GDPR, ISO 27001, and the Data Act and ensure that data can survive the threats that regulations can’t predict.
Security now means continuity. In Europe’s digital future, continuity requires architecture built for the worst day, not just the best intentions.
